Top Reasons Why Your Metabolism is Slow
Boost Metabolism Naturally: How to Tackle Age, Menopause, and Diet
Boosting your metabolism naturally can help to achieve your weight loss goals and support overall health and well-being.
This article examines several factors influencing the metabolic rate, including age, menopause, pregnancy, dieting history, and high-carb diets. It explores the role of growth hormones in metabolism and how fasting can significantly boost your metabolism.
Discover how high-carb diets lead to insulin resistance and its implications on your ability to boost metabolism naturally. By understanding the impacts of these factors and implementing suitable strategies, one can boost their metabolic rate for maximum fat-burning efficiency.
Age and Metabolism
As you age, your metabolism slows down primarily due to decreased growth hormone. Fasting and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can aid in boosting growth hormone production, thereby amplifying metabolic rate.
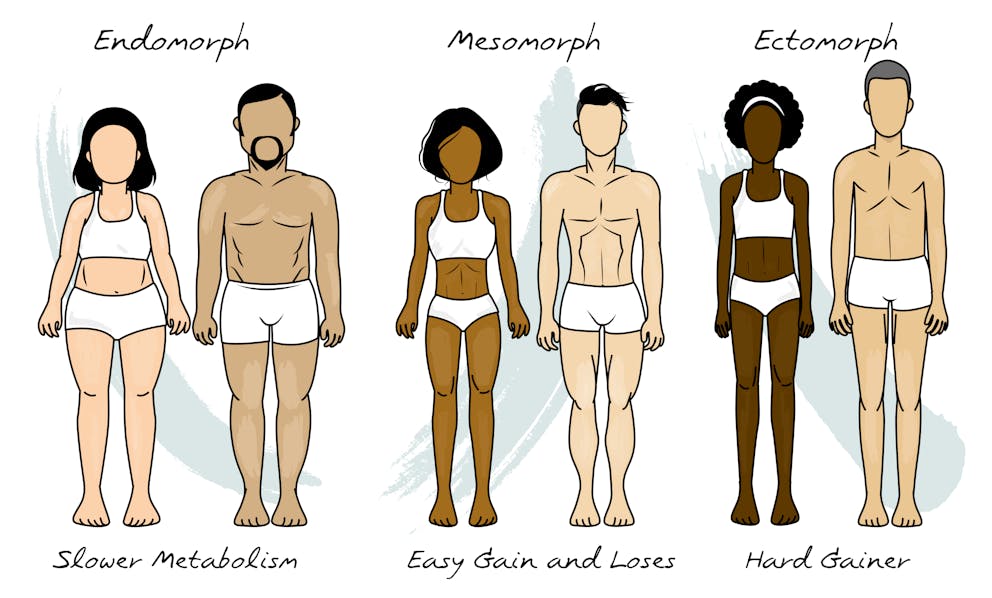
Metabolic Body Types
If you're looking to boost your metabolism, it's essential to understand that everyone has a different metabolic rate which is greatly influenced by your metabolic body types.
The Ectomorph
Ectomorphs are naturally thin individuals with fast metabolisms and little body fat. They have difficulty gaining weight and building muscle mass, making them ideal endurance athletes like long-distance runners or cyclists.
However, they may struggle with strength training and must focus on eating enough calories, healthy fats, and protein to build muscle.
The Mesomorph
Mesomorphs have an athletic build with well-defined muscles and low body fat. They respond well to strength training exercises like lifting weights, which helps them maintain their muscular physique easily.
Their metabolism is also efficient at burning carbohydrates and fats for energy, making them less prone to weight gain than other types of bodies.
The Endomorph
Endomorphic people tend to have higher body fat levels than the other two groups mentioned above. They typically have slower metabolisms that burn fewer calories daily, even when resting (basal metabolic rate).
As such, endomorphic individuals may find it challenging to lose weight through exercise alone but can benefit from adopting healthy eating habits, including avoiding sugars and carbs, while increasing fiber-rich foods and healthy fats in their diet along with regular physical activity such as walking, swimming or jogging.
The Role of Growth Hormone in Metabolism
Growth hormone is essential for maintaining a healthy body composition, promoting muscle mass development while reducing fat storage.
Growth hormone helps regulate energy expenditure by stimulating the breakdown of fats to produce fuel. Unfortunately, growth hormone production declines with age, leading to slower metabolic rates and increased difficulty losing weight.
Benefits of Fasting for Boosting Metabolism
Fasting has been shown to significantly increase growth hormone secretion, thereby helping improve metabolic function. During fasting, the body switches from using glucose as its primary energy source to burning stored fat.
This process stimulates the release of growth hormones that aid in breaking down fats more efficiently while preserving lean muscle mass.
Studies have demonstrated that intermittent fasting can enhance the ability to burn calories even at rest, making it an effective strategy for those looking to boost their metabolism naturally.
High-Intensity Interval Training as an Effective Exercise
In addition to fasting, incorporating HIIT workouts into your fitness routine can further stimulate the production of growth hormones and support optimal metabolic function. HIIT involves alternating between short bursts of intense activity and brief recovery periods.
This type of exercise increases calorie burning during the workout. It triggers what's known as the "afterburn effect," where the body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate for hours after the workout session has ended.
By combining fasting with HIIT, you can maximize your efforts in boosting metabolism and promoting healthy weight loss.
Menopause's Impact on Metabolism
Menopause is a natural biological process that signifies the end of a woman's reproductive years. It causes hormonal changes, increasing cortisol levels and altering the body's metabolism and body composition.
Supporting adrenal gland function during this period is crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolic rate.
Hormonal Changes During Menopause Affecting Metabolism
Estrogen and progesterone, essential for regulating metabolism, are the primary hormones affected by menopause.
As these hormone levels decline, women may experience weight gain due to increased cortisol production - commonly known as the "stress hormone."
Cortisol promotes fat storage, particularly around the abdomen area, making it difficult for postmenopausal women to maintain their pre-menopausal weight.
Importance of Adrenal Glands Support
The adrenal glands produce various hormones responsible for managing stress responses and regulating blood pressure. They also continue to produce small amounts of estrogen after menopause, when ovarian production declines significantly.
To support your adrenals during menopause:
Avoid excessive caffeine intake: Caffeine stimulates cortisol release from adrenal glands, and reducing caffeine intake can help lower stress levels.
Maintain regular sleep patterns: Adequate restorative sleep supports overall hormonal balance and reduces stress-related symptoms associated with menopause.
Incorporate relaxation techniques: Stretching, deep breathing techniques, or walking in nature can help manage daily stressors while promoting better mental health throughout this transitory phase.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Adrenals
To ensure optimal adrenal health during menopause, consider implementing the following lifestyle changes:
Eat a nutritious diet: Include nutrient-dense foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support adrenal function.
Exercise regularly: Engage in moderate-intensity physical activities like walking or swimming to help regulate cortisol levels and improve overall health.
Manage stress effectively: Utilize stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing exercises for better emotional well-being during menopause.
Incorporating these tips into your daily routine can significantly impact your metabolic rate during menopause. Additionally, consider exploring other natural methods like the ketogenic diet in combination with intermittent fasting to boost your metabolism further and promote overall wellness throughout this stage of life.
Pregnancy and Estrogen Levels
A history of pregnancies may affect your metabolic rate by causing elevated estrogen levels. Consuming plenty of cruciferous vegetables is crucial to regulate estrogen and prevent excessive fat storage while avoiding dairy products, soy, and other estrogenic foods.
How Pregnancy Affects Estrogen Levels
During pregnancy, the body experiences a significant increase in estrogen levels. This hormone is crucial in supporting fetal development but can lead to weight gain if not appropriately regulated after childbirth.
Elevated estrogen levels may cause the body to store more fat, making it difficult for women with multiple pregnancies to lose weight effectively.
The Role of Cruciferous Vegetables in Regulating Hormones
Consider incorporating cruciferous vegetables into your diet to help balance hormones post-pregnancy and boost metabolism naturally.
These nutrient-dense vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and Brussels sprouts contain indole-3-carbinol (I3C), which helps detoxify excess estrogens from the body.
Consuming cruciferous vegetables and following a low-carb ketogenic diet like Healthy Keto® in combination with intermittent fasting helps maintain the optimal hormonal balance necessary for efficient metabolism.
Foods Rich in Cruciferous Vegetables:
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Kale
Brussels sprouts
Bok choy
Arugula
Cabbage
Collard greens
Foods to Avoid Increased Estrogen
In addition to consuming cruciferous vegetables, avoiding foods that may increase estrogen levels and slow down your metabolic rate is essential. Some common foods to limit or avoid that may increase estrogen levels and impede weight loss efforts include dairy products, flaxseeds, soy-based items, and certain legumes, specifically:
Flax seeds
Soy-based foods, including tofu and tempeh
Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas high in phytoestrogens
Pregnancy triggers several pathways that can affect hormonal balance, especially estrogen. Making the right dietary choices and practicing stress-reduction techniques can significantly improve hormonal balance and promote a healthy metabolic rate.
Frequent Dieting and Slow Metabolism
Over time, long-term restriction of caloric intake can cause the metabolism to slow down, leading to a decreased ability for weight loss due to the body's adaptation to conserve energy.
The body adapts to the reduced calorie intake by conserving energy, ultimately hindering weight loss efforts.
Instead of cutting calories drastically, focusing on nutrient-dense meals rich in healthy fats is essential to provide sustainable energy and ample nutrients needed for metabolic processes.
Adverse Effects of Long-Term Low-Calorie Diets on Metabolism
Prolonged low-calorie diets may cause a persistent decrease in your resting metabolic rate, which can lead to weight gain and difficulty losing weight. A lower metabolic rate means fewer calories are burned at rest, leading to a slower overall metabolism.
Prolonged caloric limitation may also cause muscle deterioration, reducing metabolic rate since muscles are more metabolically active than other body tissues.
Nutrient-Dense Meal Planning Tips
Eat whole foods: Look for unprocessed foods such as healthy fats, proteins, vegetables, and berries, while limiting carbs and sugars.
Incorporate fiber-rich foods: Fiber helps keep you full longer while supporting digestive health. Include plenty of leafy greens and other high-fiber vegetables in your meals.
Avoid empty calories: Avoid sugary drinks and processed snacks that provide little nutritional value but contribute significantly towards daily calorie intake.
The Benefits of Keto for Improved Metabolic Rates
Keto is a high-fat, low-carb diet that has been shown to improve metabolic rates by promoting fat burning as the primary energy source. This dietary approach helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing insulin resistance and supporting healthy weight loss.
Additionally, combining keto with intermittent fasting can enhance metabolism by allowing your body to enter a state of ketosis more efficiently during fasting periods.
In this state, your body burns stored body fat for fuel instead of relying on glucose from carbohydrates.
Incorporating nutrient-dense meals, keto principles, and intermittent fasting into your lifestyle can help counteract the adverse effects of long-term low-calorie diets on your metabolism.
By focusing on these strategies, you'll be better equipped to maintain a healthy metabolic rate while achieving sustainable weight loss results.
High-carb Diets Lead to Insulin Resistance
Consuming high-carb diets regularly can lead to insulin resistance, resulting in increased fat storage and an impaired ability to burn fat efficiently. Excessive carbohydrates and sugars cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, prompting the pancreas to release more insulin.
Over time, this constant demand for insulin can make cells resistant and less responsive, which can harm your metabolism.
The Vicious Cycle of High-Carb Diets and Insulin Resistance
A diet high in carbs and sugars triggers a vicious cycle that makes it hard for your body to sustain normal blood sugar levels and utilize stored fats as an energy source. Here’s how sugars and carbs trigger blood sugar imbalances:
You consume large amounts of carbohydrates.
Your blood sugar levels rise rapidly.
Your pancreas releases insulin to help lower blood sugar.
Over time, your cells become resistant due to frequent insulin exposure.
This resistance forces your pancreas to produce excessive insulin levels to compensate for the lack of cellular response, which worsens insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance, left untreated, can hinder weight loss and contribute to serious health issues such as type-2 diabetes.

Keto Diet: A Low-Carb Solution for Better Metabolic Health
To combat the adverse effects on metabolism caused by high-carb diets, consider adopting a low-carb ketogenic diet plan. Limiting carb intake and increasing healthy fats helps to keep blood sugar levels steady, which prevents insulin spikes and promotes better metabolic health.
The keto diet has been shown to:
Improve insulin sensitivity
Promote weight loss and fat-burning
Enhance energy levels and mental clarity
To get started with a keto diet, limit starches, sugars, and carbs and focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods such as leafy greens, healthy fats like avocado and coconut oil, organic grass-fed beef, or wild-caught game meat and fish. Limiting carb intake to no more than 20 to 50 grams daily is recommended to promote fat-burning and ketosis.
Intermittent Fasting: A Complementary Strategy to Manage Insulin Sensitivity
In addition to adopting a low-carb diet plan like the ketogenic diet, intermittent fasting (IF) can also help improve insulin sensitivity by allowing your body more time between meals to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
IF involves cycling between eating and fasting throughout the day or week. This practice has been linked to improved metabolic health and other benefits, such as increased longevity and better cognitive function.
Metabolism Mystery
Understanding why metabolism slows down can often be a puzzle. Factors such as age, hormonal changes, and lack of physical activity can contribute to this slowdown.
Using a Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) calculator can shed light on how many calories your body burns in a day, which is crucial for managing weight and optimizing metabolism.
By incorporating regular exercise, especially strength training, and making dietary adjustments to ensure sufficient protein intake and balanced nutrition, you can effectively support your metabolism and maintain overall health.
Tracking these aspects with a TDEE calculator provides valuable insights into achieving metabolic balance and vitality.
Conclusion
Enhancing metabolic rate naturally is essential to achieving a healthy body weight and promoting metabolic health.
There are various ways to increase your metabolic rate, such as incorporating plenty of cruciferous vegetables into your diet, fasting, high-intensity interval training, and a nutrient-dense high-fat diet like Healthy Keto.
FAQs
1. How Can I Naturally Increase My Metabolism?
To naturally increase your metabolism, incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT), maintain a nutrient-dense low-carb diet, and practice intermittent fasting.
Additionally, support adrenal health with stress management techniques and consume cruciferous vegetables to regulate hormone balance.
2. Is It Possible to Naturally Increase Metabolism?
Yes, it is possible to naturally increase metabolism through various lifestyle changes, such as adopting a ketogenic diet, engaging in regular exercise like HIIT workouts, and optimizing hormonal balance by regularly consuming cruciferous vegetables.
3. What's a Good Natural Metabolism Booster?
An excellent natural metabolism booster includes practices like intermittent fasting that help elevate growth hormone levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
4. What Boosts Metabolism?
Scientifically proven methods for boosting metabolism include high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which increases post-exercise oxygen consumption; the ketogenic diet that enhances fat oxidation; intermittent fasting, which promotes growth hormone secretion; and proper sleep hygiene, which supports overall hormonal balance.
Previous blog
The BEST Motivation to Lose Weight
Popular
08/21/2024
47.3K views
05/22/2024
41.4K views
11/18/2024
245.7K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




